
Parenthood Sets Women, But Not Men, on a Path of Lower Lifetime Earnings
In the most equal workforces, motherhood drives the gender pay gap.

New Zealand’s Prime Minister, Jacinda Ardern, is about to become a first-time parent next month, and her partner, Clarke Gayford, will set an example by becoming a stay-at-home dad.
But Jacinda and Clarke’s plan is still the exception rather than the rule. Mothers tend to take more time than fathers away from their careers when they have children, and they pay a significant price.
Our recent research shows how parenthood contributes to the gender pay gap. It penalizes all women, particularly those who are on high incomes, and sets them on a trajectory of lower lifetime earnings relative to their male peers.
Gendered response to parenthood
In New Zealand, the gender pay gap has fallen over the past 20 years and it is now below 10%. Earlier research shows that a high proportion of the gender pay gap can’t be explained by differences in observable information, such as age, education, occupation and industry, and nor is it due to differences in productivity.
New Zealand is similar to the rest of the world in that the gender pay gap is larger among parents than people without children, although the reasons for this are not entirely clear. Our research uses newly combined data to describe what happens to men’s and women’s employment and wages after they become parents.
It shows a strongly gendered labour response to parenthood: Women dramatically decrease their employment and work fewer hours if they are employed, whereas men’s employment and hours worked barely change. Mothers, particularly those with high incomes before parenthood, experience lower monthly incomes and hourly wages than before they had children.
These reductions are larger the longer they are away from paid work, and persist for at least 10 years. Furthermore, high-income women who return to paid employment soon after becoming parents experience dramatically and persistently slower rates of income growth compared to before. They are therefore likely to have much lower lifetime earnings than similarly high-income men who become fathers.
Changes in employment and earnings for women after giving birth are likely to be related to social norms as well as the ability to breastfeed. We need to ask why so few men become the primary caregiver of their children?
Employment gaps
Our work shows that few men stop paid employment after having a child, but only three out of five first-time mothers do any paid work before their child’s first birthday.
Women with higher incomes and those with higher qualifications before parenthood return more quickly to work after childbearing and maintain higher employment rates. Only 45% of mothers with no qualifications are employed 10 years after their first baby, compared with over 60% of those with a school or higher qualification and nearly 70% of those with a bachelor’s degree.
Women who became mothers when aged 25 to 34 have higher employment rates after having children than older women. The employment rate of those who became mothers when aged under 25 is lowest (only 34% in their child’s second year). Before becoming mothers, Māori and Pacific women are far more likely not to be employed than Pākehā (New Zealander of European descent) women, but this gap narrows in percentage point terms after they become mothers. Pākehā mothers have a 59% employment rate in their child’s tenth year compared with 41% for Pacific mothers and 45% for Māori mothers.
Monthly wage earnings
Monthly wage earnings are driven by a combination of hourly wages and monthly hours worked. They are important for a parent’s ability to support his or her family and for lifetime earnings. Across every pre-parenthood income quartile, employed women experience decreases in monthly earnings when they have children, while men do not. The decreases are larger for women who return to work more slowly.
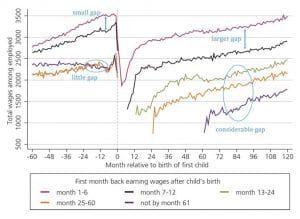
This graph shows the change in monthly earnings by time out of employment. Sin, Dasgupta and Pacheco (2018) Parenthood and labour market outcomes, CC BY.
Time out of employment matters more for high-income women, but even those who return to work quickly experience much slower income growth after becoming parents. Prior to parenthood, these women were on a trajectory to be very high earners, and the dampening of their income growth helps explain why relatively few women appear in the highest income brackets. Their fast return to employment does, however, increase their earnings lead over their slower-returning colleagues.
In contrast, low-income women who are employed experience small monthly income decreases with parenthood and similar income growth rates before and after having children. However, this isn’t necessarily a positive sign, as it could merely indicate that they were underemployed before motherhood.
In terms of ethnic differences, monthly income for Māori, Pacific Peoples and Asian mothers in paid employment is slightly higher in the second year after their child’s birth than in the second year before it. Over the same period, employed Pākehā mothers experience the largest decrease in monthly income.
Work hours and wages
Employed mothers work a median of 27 hours, down from a pre-parenthood median of 40 hours. The longer a woman spends out of work the fewer hours she works on average upon her return. Women who return to work in the first six months work a median of 30 hours, those who returned in months 7 to 12 work a median of 27 hours, and those who return after month 12 work a median of 22 hours. Men work a median of 41 hours both before and after becoming parents.

This graph shows the changes in hours for employed women, by time out of employment. Sin, Dasgupta and Pacheco (2018) Parenthood and labour market outcomes, CC BY-SA.
It isn’t just a decrease in hours that contributes to the wage gap. Across our sample (which is not representative of the population and so differs from the official gender wage gap), women earn 6.8% lower hourly wages than men of the same age and education. The wage difference is 5.7% between men and women without children, but 12.5% between men and women who are parents.
When men become parents, their hourly wages aren’t significantly affected. Women, on the other hand, pay a price. Their hourly wages decrease by 4.4% compared with the wages they could have expected without children. This wage penalty for motherhood varies substantially with how long the woman stays at home. The longer they stay at home, the bigger the drop in their hourly wages. Only some of this drop in pay can be explained by mothers moving to lower-paying industries and occupations.
Our research shows that parenthood exacerbates pre-parenthood gender wage gaps, with time out of work and reduced hours both playing major roles. We believe that we won’t see equality in the labour market until it is just as common for a dad to stay home with the kids as it is for a mum. While many mothers may want to take time away from work to raise their children, this should be a personal (or family) choice and not the result of traditional gender roles.
This article was originally published on The Conversation.

Isabelle Sin is a lecturer in economics and econometrics at Victoria University and a Fellow with Motu Economic and Public Policy Research at Victoria University of Wellington. Gail Pacheco is a professor of economics and director of the NZ Work Research Institute at Auckland University of Technology.
Related


Indian Women Aren’t Managing Their Own Finances
